Lead Management Tool – Automating Lead Conversion with Smart Rules
Project Overview
The Lead Management Tool is a centralized platform that helps businesses clean, map, and convert raw lead data into potential opportunities using automation and smart rules.
Designed for Managers and Admins, the tool removes friction from lead processing by offering:
CRM Field Mapping
Visual Rule Builder
Execution Logs
Role-Based Access
This product matters because it eliminates manual workflows, reduces lead loss, and empowers teams with visibility and control—without relying on engineering for every change.
Problem Statement & Goals
Business Need
As lead volume scaled, managing lead imports across departments became fragmented. Teams relied on spreadsheets, manual mapping, and error-prone data cleanups—leading to lost leads and inconsistent conversions.
Core Pain Points
Repetitive lead uploads with inconsistent formats
Manual field mapping for every import
No way to track how leads were modified
Managers lacked oversight of rule executions
Errors went unnoticed until too late
Goal
Reduce manual effort in lead mapping and rule processing
Improve accuracy and speed of lead-to-opportunity conversion
Provide audit-ready visibility into every automation step
Enable Admins to create pipelines; Managers to oversee results
Users & Roles
Admin: Creates and configures pipelines, field mappings, rule logic
Manager: Views mapped data, tracks rule execution, and oversees lead quality
Design Process
Discovery
The project began with understanding the real challenges on the ground.
I scheduled interviews with Sales Ops, Admins, and CRM Heads, focusing on how they currently imported leads and where things broke down.
What emerged was a recurring pattern:
Duplicate leads clogging the CRM
Mapping fatigue, where users had to manually align fields for every import
Zero post-upload visibility, meaning teams didn’t know what rules ran, which leads failed, or why
I mapped their existing workflows step-by-step and created a pain-point heatmap to visualize where inefficiencies occurred most often. This helped align the team on what problems were worth solving first.
Define
With research insights in place, I moved into problem scoping and flow definition.
I sketched task flows for three critical activities:
Uploading and mapping leads
Applying conditional logic via the rule engine
Reviewing execution logs to understand what happened after a rule was applied
The guiding principles were clarity (every step should be obvious), validation (errors caught early), and reusability (mappings and rules could be saved and reused).
By the end of this stage, I had a clear blueprint of the product’s backbone — not just what features to build, but how they would fit together in a seamless experience.
Design
The design phase began with low-fidelity wireframes, where I experimented with different flows. After testing early sketches with stakeholders, we arrived at a 5-step pipeline wizard that kept the process simple yet powerful.
Key design highlights:
Visual Rule Builder: Inspired by “if-this-then-that” logic, allowing users to set up rules in plain language without touching code.
Role-Based Views: Admins had full control (create, edit, delete), while Managers had a read-only dashboard for oversight.
Smart Field Mapping: Added auto-suggested matches for frequently mapped fields, reducing cognitive load and setup time.
Throughout the design process, I iterated heavily — especially on mapping screens — balancing functionality with minimal cognitive friction.
Validation
Once we had a clickable prototype in Figma, we conducted usability testing with internal Sales and Ops teams. The feedback loop was invaluable.
Three major improvements came directly from user feedback:
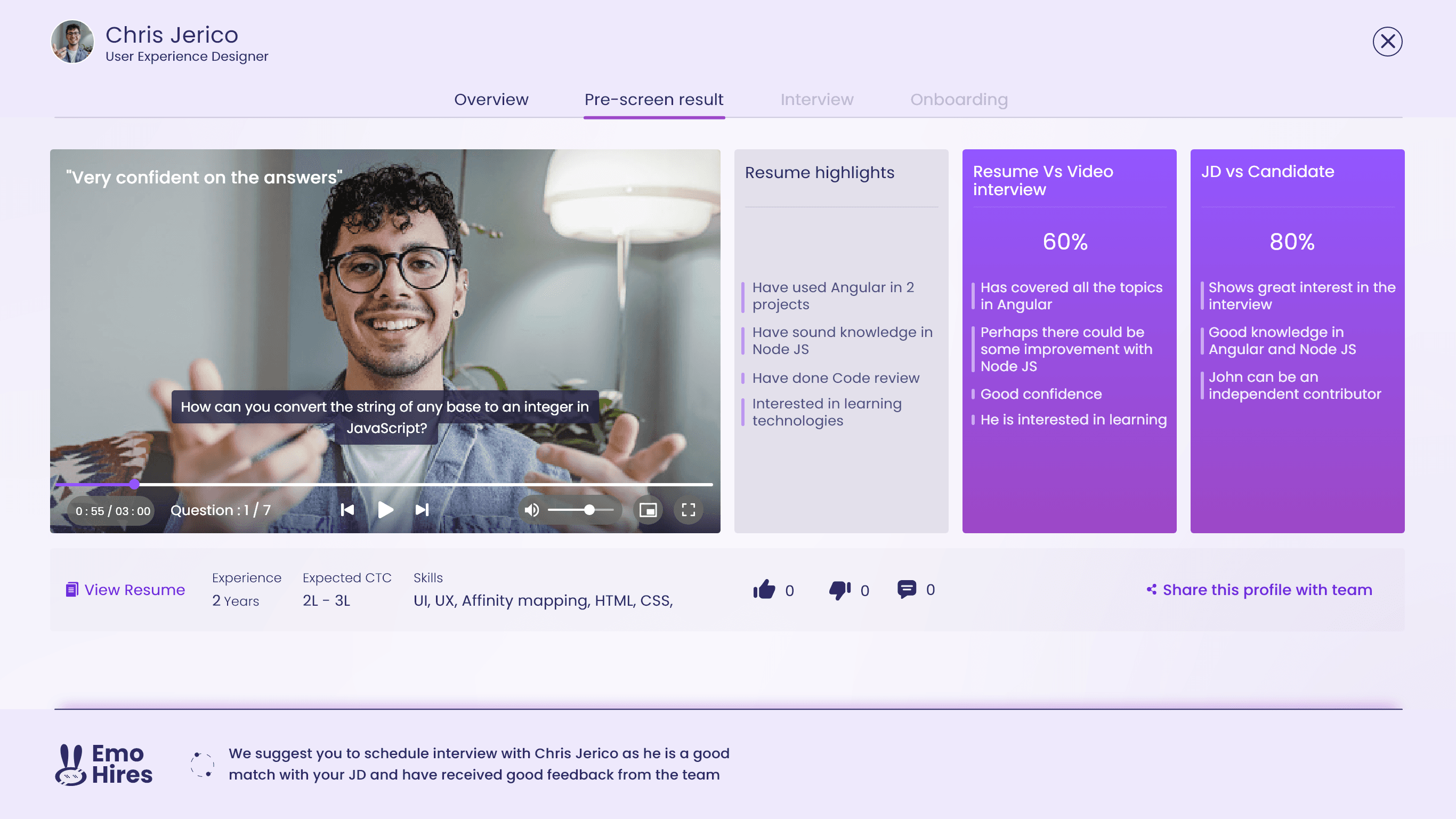
More human-readable logs – Added natural language summaries so anyone could understand what happened to a lead.
Rule Preview before Activation – Letting users verify logic before going live reduced accidental misconfigurations.
Simplified Mapping UI – Grouped fields into toggle-based categories, cutting setup time nearly in half.
After three iteration rounds, I finalized the prototype and delivered ready-for-dev specs in Figma, complete with component states and interaction notes.
Opportunities and challenges
OPPORTUNITY
From the first round of research, it was clear this product could deliver high-impact wins for both business efficiency and user satisfaction:
Centralizing lead operations into a single, role-based tool meant no more juggling between spreadsheets, CRMs, and email threads.
Automation through the rule engine had the potential to cut down repetitive data-cleaning tasks, freeing managers and admins to focus on conversion strategies.
Data visibility via execution logs could transform decision-making — giving managers real-time clarity on lead outcomes and rule performance.
Reusable mappings and rules could make onboarding new team members faster and reduce training costs.
CHALLENGES
Designing the product wasn’t without hurdles:
Complex logic for diverse roles — Admins needed full control while Managers required a simplified, oversight-focused interface.
Preventing accidental data overwrites when multiple rules ran on the same lead simultaneously.
Making automation trustworthy — users needed to understand why a lead was modified, not just see that it was.
Minimizing mapping fatigue — balancing flexibility for different CRMs with intelligent defaults to save time.
Scaling UI complexity — the more conditions and actions added to the rule builder, the harder it became to maintain a clean, non-intimidating design.
Interviews
Qualitative interview
I connected with Sales Operations Managers, CRM Administrators, and Regional Sales Heads to understand their challenges in lead imports and pipeline automation. They emphasized the need for faster, more reliable lead onboarding to avoid missed opportunities. Common frustrations included repetitive field mapping, duplicate entries, and lack of visibility into rule execution results.
While participants had varying workflows depending on team size and CRM setup, all agreed that automation could save time, improve lead quality, and reduce post-import troubleshooting. These insights shaped our approach to designing a streamlined, rules-based pipeline tool.
Findings from interviews
Interview insight #01
Interview insight #01 – Repetitive Mapping Fatigue
Sales teams reported having to manually map lead fields every time they imported data, even when similar templates were used. This led to wasted time and inconsistent mappings. They wanted an auto-suggest feature and the ability to save mapping templates for reuse.
Interview insight #02
Interview insight #02 – Duplicate Lead Overload
Without proper validation, duplicate leads were slipping into the system, creating confusion for sales reps and affecting reporting accuracy. Teams requested an automated deduplication process during upload.
Interview insight #03
Interview insight #03 – Zero Visibility Post-Upload
After importing leads and applying rules, users had no easy way to check what happened next. Missing leads, rule failures, or incorrect field values were discovered only later. Stakeholders highlighted the need for clear, human-readable execution logs.
Building empathy
Using the qualitative data from interviews, I defined the three target group profiles Sarah (Recruiter, Talent Acquisition Manager), John (Recruiter, Founder of a Tech Startup), Emily (Candidate, Software Engineer) to better empathize with my main user groups and prioritize goals according to their needs
Riya Sharma
Riya manages all inbound lead data for a mid-sized B2B sales company. Her day often starts with raw Excel sheets from marketing, event sign-ups, or partner uploads. She spends hours importing leads into the CRM, ensuring field mappings are correct, and checking that no duplicates or bad data slip through. She’s meticulous but feels bogged down by repetitive manual work.
Pain points
Manually mapping the same fields every week is exhausting.
Duplicate leads clutter the CRM, causing sales reps to complain.
No quick way to identify and fix upload errors.
Lacks a clear audit trail of which rules were applied to each upload.
Time lost switching between spreadsheets and CRM.
Field names vary wildly in source files, creating confusion.
Cannot easily automate routine checks without IT help.
Goals
Upload leads quickly without repeated manual mapping.
Keep the CRM clean and duplicate-free.
Gain better visibility into the lead processing steps.
Reduce upload errors and retries.
Reuse mappings and rules across multiple uploads.
Trust that automation is doing the right work in the background.
Spend more time on strategic improvements, not repetitive admin work.
Arjun Mehta
Sales Manager – B2B Enterprise Accounts
Arjun oversees a team of sales reps who rely on high-quality leads to hit monthly targets. He’s not involved in the nitty-gritty of importing data but depends heavily on the accuracy and timing of that data. When poor-quality or incomplete leads make it into the pipeline, his team wastes hours chasing dead ends. Arjun values transparency—he wants to know where leads come from, what rules have been applied, and how opportunities are progressing.
Pain points
Leads sometimes reach his team without proper qualification.
No easy way to verify how leads were processed or filtered.
Delays in getting new leads into the pipeline slow down sales cycles.
Inconsistent field mapping causes missing or misplaced info in CRM.
Hard to trace back which rule caused certain leads to be included or excluded.
Wants less dependency on Admins for data explanations.
Limited visibility into the performance of lead processing rules.
Goals
Access clean, qualified leads in real time.
Quickly view a lead’s journey—source, mapping, and rules applied.
Improve his team’s conversion rate with better-targeted opportunities.
Trust that the rule engine is filtering leads correctly.
Reduce back-and-forth with Admins for clarifications.
Monitor the health of the pipeline with high-level dashboards.
Use lead insights to refine sales strategies and campaigns.
Task model
—————————————————————— ——- - - - - - - - -
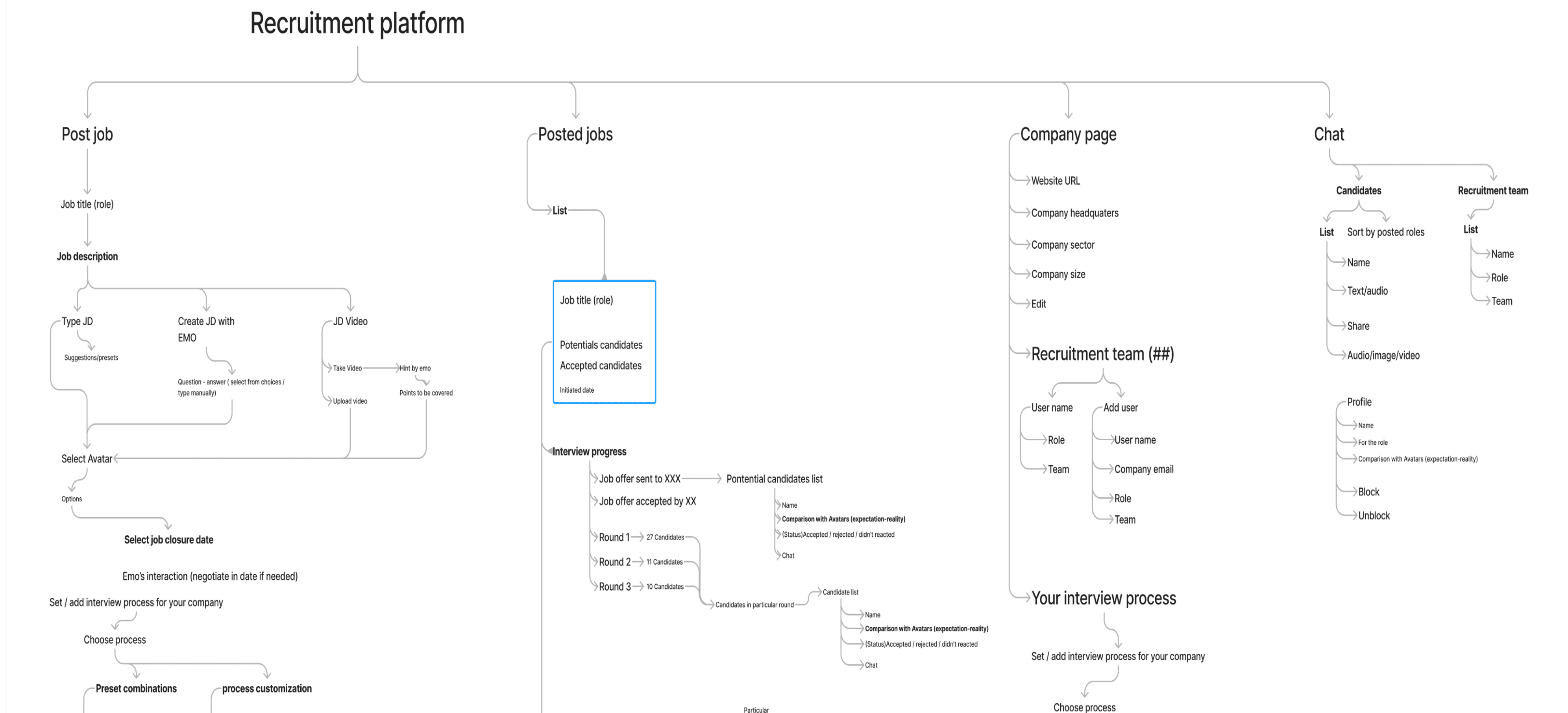
Information architecture
Based on the insights gained from the initial content audits, competitor analyzes and Card Sorts with potential users, I defined the sitemap for the product. - - - - - - - ————— - - - - - - -
Key features
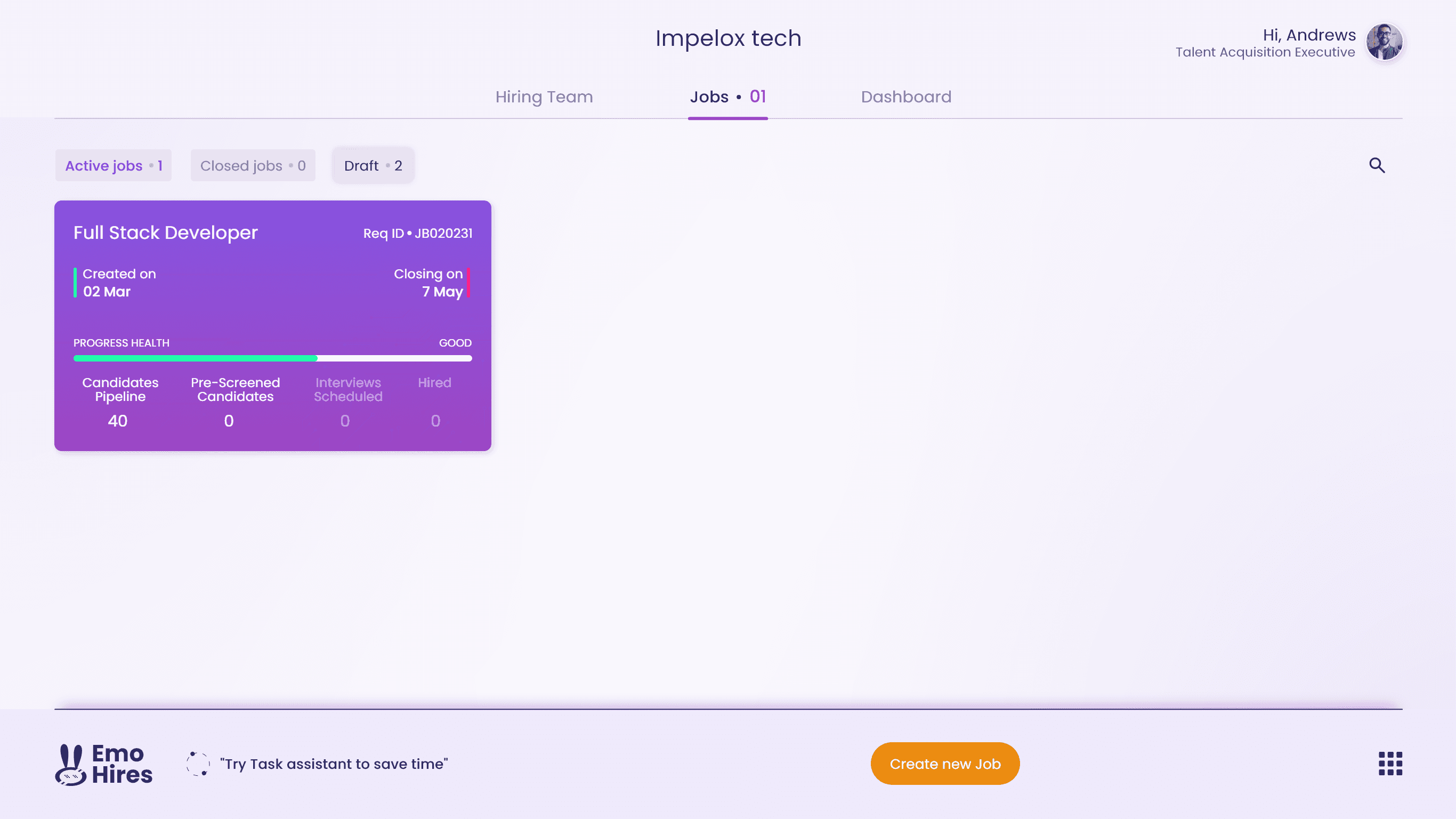
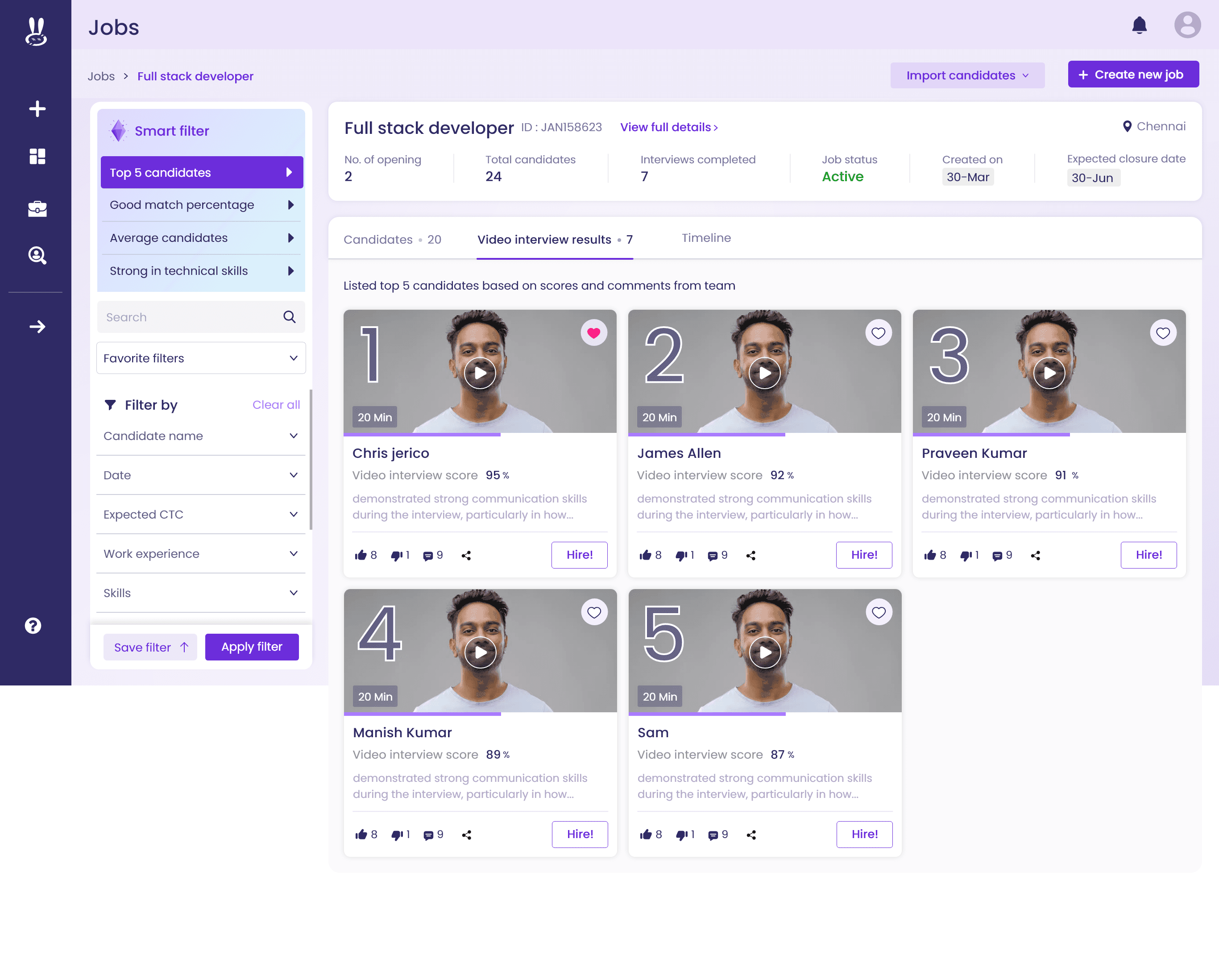
Pipeline Creation Wizard (5 Steps)
Guided flow for creating, editing, and deleting pipelines.
Steps: Basic Details → Import Raw Leads → Field Mapping → Opportunity Mapping → Rule Engine.
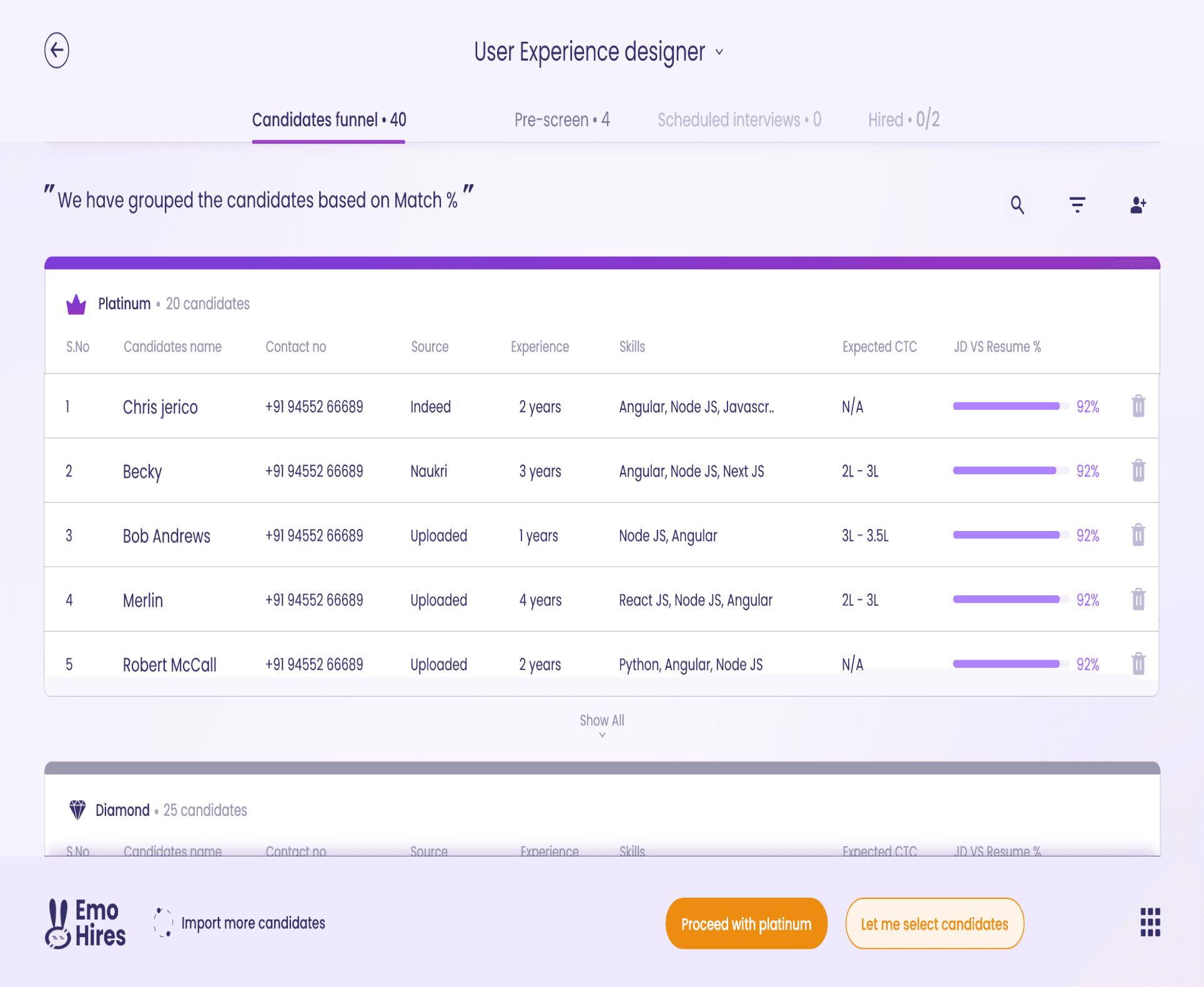
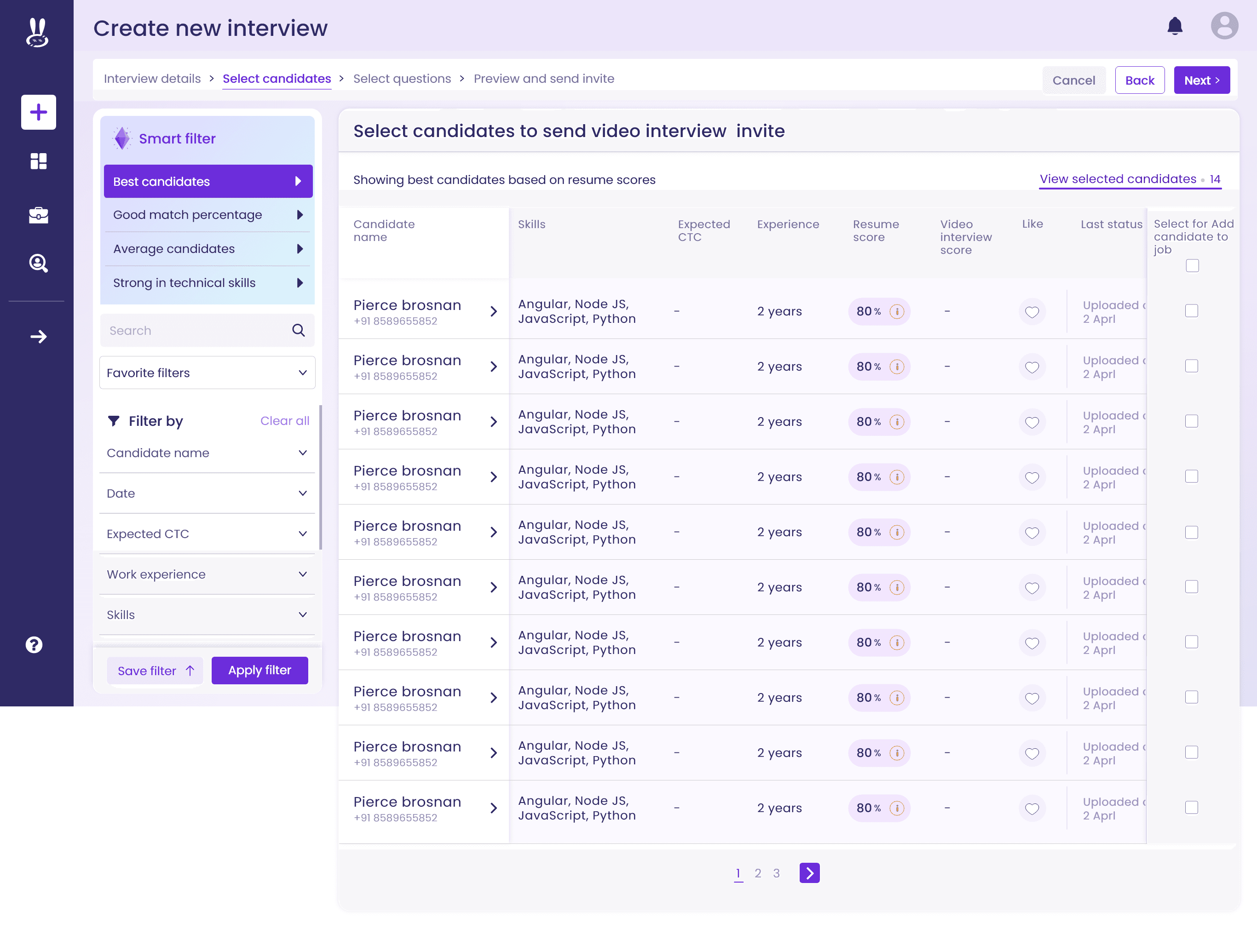
Field Mapping with Auto-Suggestions
Matches raw Excel columns to CRM fields.
Saves mapping templates for reuse to reduce repetitive work.
Opportunity Mapping
Link leads to business opportunities (e.g., Zoho, Salesforce) with mandatory & optional fields.
Allows selective inclusion of extra fields.
Visual Rule Engine
If–Else–And–Or logic builder with multiple triggers (upload, update, custom, scheduled).
Ability to chain rules so one action triggers another.
Execution Logs
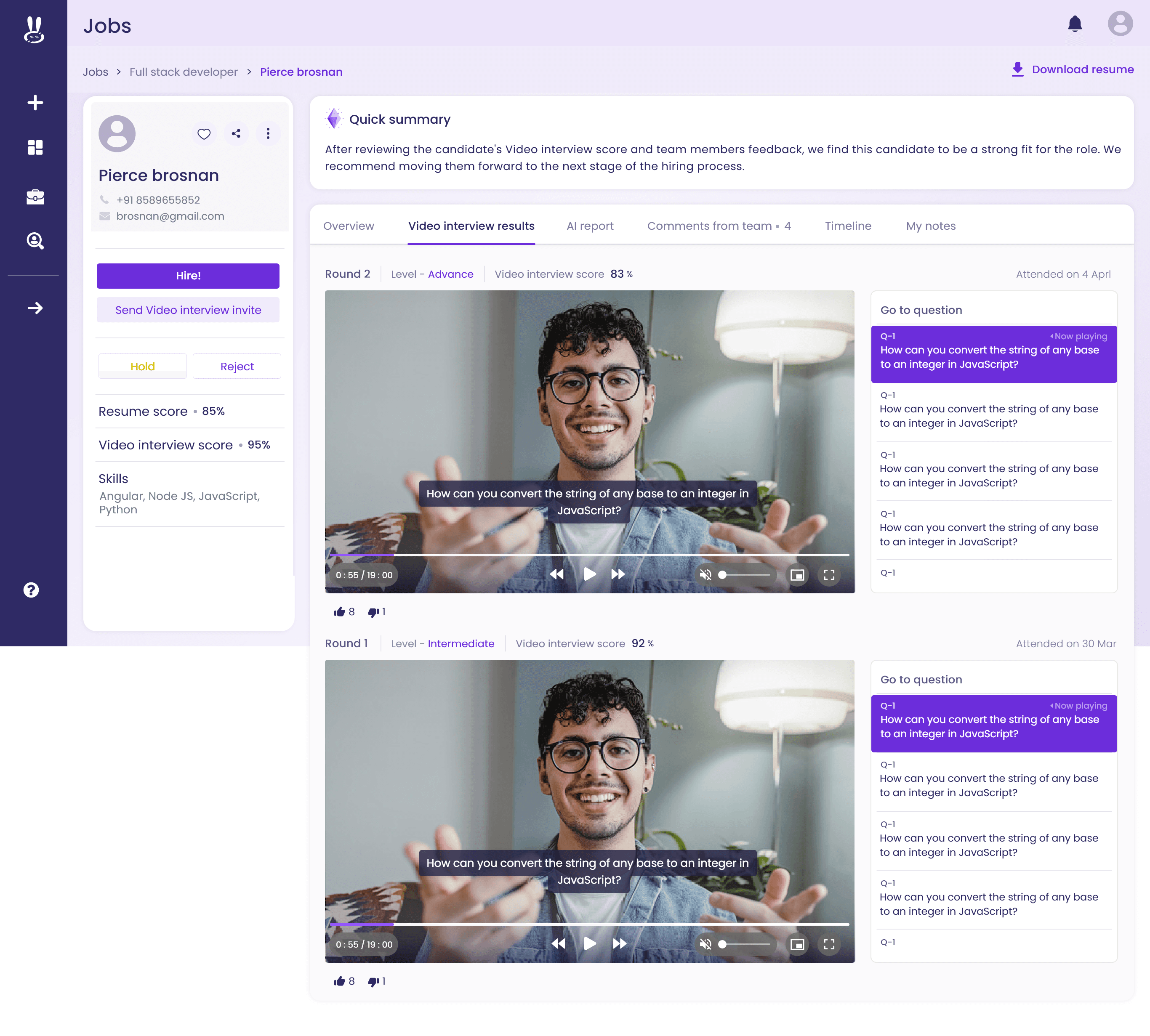
Human-readable history of rule runs, lead changes, and outcomes.
Exportable for compliance and auditing.
Role-Based Access
Admins: Create/edit pipelines, rules, and mappings.
Managers: View-only dashboards, performance metrics, and rule outcomes.
Data Validation & Error Handling
Detects duplicates and incomplete leads before they enter the pipeline.
Upload success/failure summary post-import.
KPIs
0% Reduction in ticket resolution time by removing manual clarification loops.
40% Fewer Duplicate Leads through improved validation & rule-based filtering.
25% Faster Lead Onboarding thanks to saved field mapping templates.
Increased Manager Oversight with real-time logs and opportunity tracking.
Positive Feedback from sales teams on clarity of rule outcomes and mapping UI.
Higher Reuse Rate of saved mapping templates across different teams (tracked via analytics).
Learnings
Logs were initially an afterthought—but became a top feature. Users wanted to see what happened in every upload.
Visual rule logic felt intuitive, even to non-technical users—especially when preview + nested logic was added.
The biggest surprise? Users loved auto-suggestions in field mapping. It saved them cognitive load.
Wireframes, prototype & usability-testing
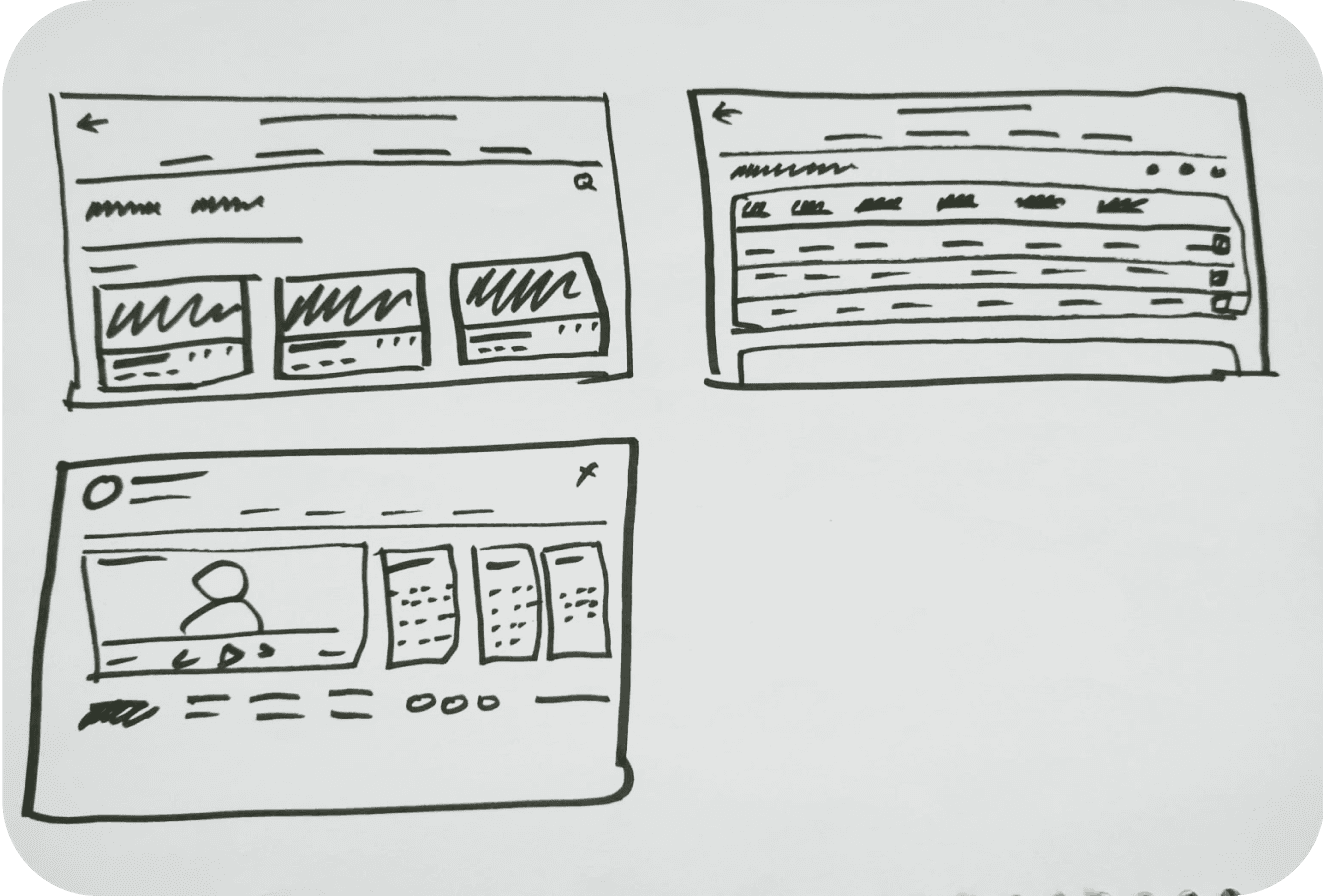
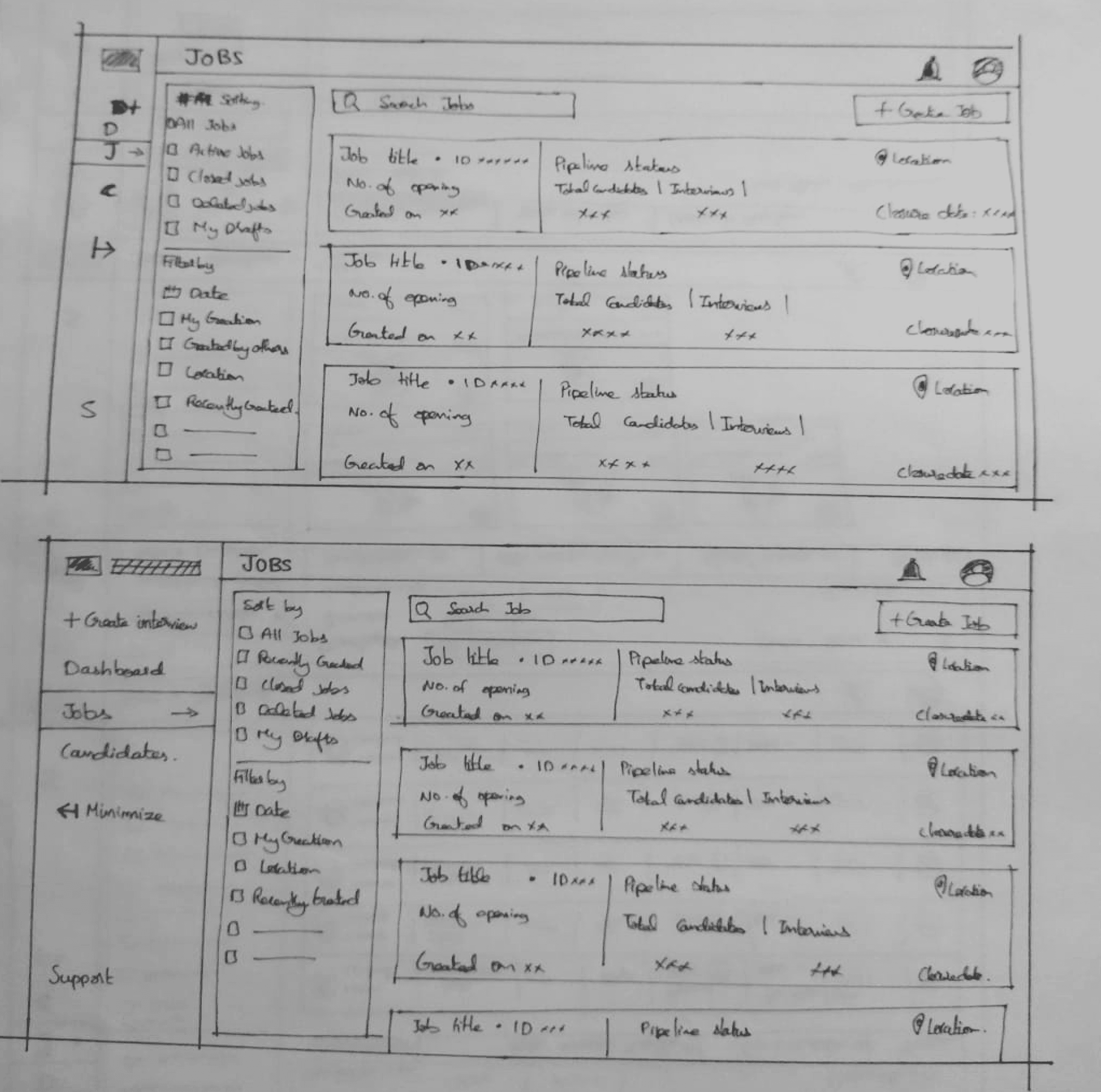
Paper-prototype
Wireframes
Contextual generative AI footer
Wireframes
Usability-testing
What worked
What didn’t worked
Iteration based on insights from usability testing
Paper-prototype
Iterated Wireframes
Key Takeaways
Conclusion